

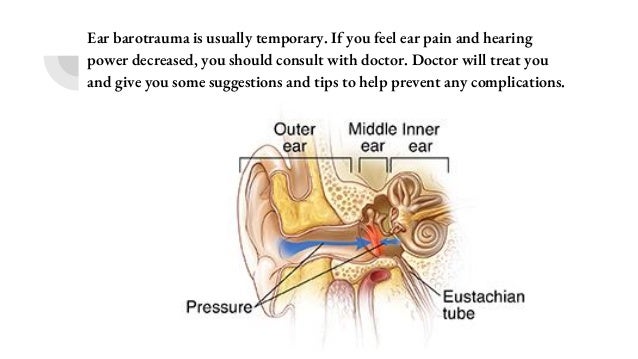
To help prevent ear barotrauma from ear infections and other illnesses, keep your ears clean and dry. Treatment for Inner Ear Barotrauma Avoid equalising the ears (even if you feel fullness) Do not put drops in the ear canal Nasal decongestant sprays may. Diving again before you’ve fully recovered could lead to further injury. Lung over-pressure injury may require a chest drain to remove air from the pleura or mediastinum. Treatment of diving barotrauma depends on the symptoms, which depend on the affected tissues. If you have recently experienced ear barotrauma, be sure to stay on dry land until your ears have fully recovered. Medication Summary The primary medications in treatment of dysbaric injuries are oxygen, oxygen-helium, 38, 39, 40 isotonic fluids, anti-inflammatory medications, decongestants, and. Inner ear barotrauma (IEBt), though much less common than MEBT, shares a similar external cause. Ignoring this warning sign could leave your ears injured more permanently. If you start to feel pain while diving, make your way back to the surface slowly. Decongestants are used to reduce the pressure differential. Sinus and middle ear squeeze are treated identically. If you plan to go scuba diving, it can be a good idea to not only equalise your ears before you hop in the water and as you descend, but to also head into the water feet first. The primary medications in treatment of dysbaric injuries are oxygen, oxygen-helium, 38, 39, 40 isotonic fluids, anti-inflammatory medications, decongestants, and analgesics. When travelling by plane, try to also stay awake throughout the take-off and landing. To help reduce your chances of experiencing ear barotrauma, you might consider using earplugs designed for air travel, which may help to slow the effects of pressure changes, or taking decongestants or antihistamines before you fly.
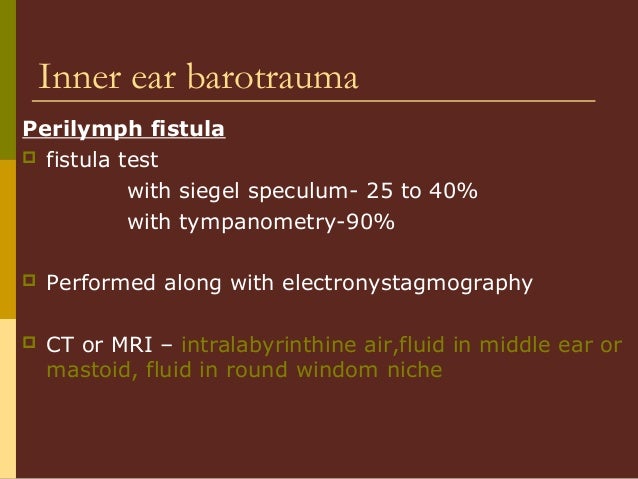
In conclusion, we suggested that steroid administration would be effective for the treatment of inner ear barotraumas.It’s normal to experience ear barotrauma occasionally, especially when you’re travelling, but recurring and severe cases are best avoided where possible. When compared two groups in the moderately to severely damaged ears, the hearing threshold shift of the treatment group was significantly lower than that of the control group at 2 and 7 weeks after pressure loading (non paired t-test, p<0.01 and p<0.05). The mainstay of treatment for alternobaric vertigo is re-establishing the pressure equilibrium between the two middle ears. The time course change of the healing threshold shift was significantly different between the two groups (repeated measured ANOVA, p<0.05), and the healing threshold shift was more remarkable in the treatment group. The time course change of the healing threshold shift was compared between the two groups. Before, just after pressure loading, 2, 3, 5, and 7 weeks after pressure loading, auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing was performed, and the healing threshold shift was evaluated.
If symptoms are continuing, diagnosis typically involves finding. In the treatment group, guinea pigs were administrated with dexamethasone at a dose of 2.0mg/kg/day intraperitoneally once a day for 5days after the pressure loading. But if the eardrum (tympanic membrane) has ruptured, it could several months to fully recover. The guinea pigs that had hearing threshold shift were randomly divided into steroid administrated group (treatment group)(19 ears) and control group (16 ears). Guinea pigs were subjected to rapid compression and decompression between 1 absolute pressure (ATA) and 2 ATA in a chamber within 5 seconds.

The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of steroid administration for inner ear barotrauma in the experimental study. Several authors reported the effect of steroid administration for inner ear barotrauma as clinical results, however, there is no experimental study to prove its effect.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
